

Ireland: Kerry - Dublin - Cork - Waterford - Roscommon - Galway - Belfast
UK: London - Manchester - Newcastle - Cardiff - Liverpool
Brazilian waterweed
Invasive Species Information

What Is Brazilian waterweed - (Egeria densa)?
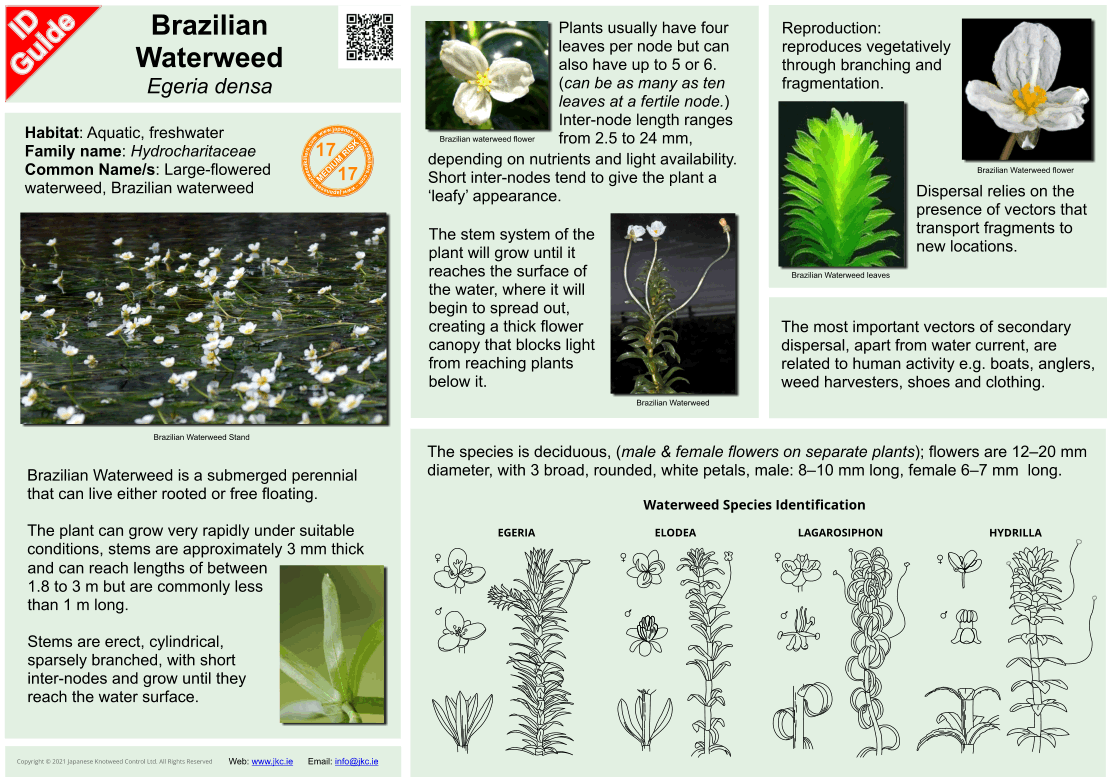
Habitat: Aquatic, fresh water
Distribution in Ireland: Sparse distribution but locally abundant in some places.
Status: Established
Family name: Hydrocharitaceae
Common name/s: Large-flowered waterweed, Dense waterweed, Anacharis
Reproduction: Typically displays little variation in growth patterns throughout the year when grown in tropical
environments, however, when grown in more moderate
environments the plant spends most of its energy on starch production and storage in the winter and canopy growth during the summer season. Can spread through transport of plant fragments.

Brazilian waterweed flower and stem

Brazilian waterweed leaf
Brazilian Waterweed is an Aquatic plant native to Argentina, Brazil, and Uruguay, growing in water up to 4 m deep, with trailing stems to 2 m or more long, producing roots at intervals along the stem.
Leaves are produced in whorls of four to eight, 1–4 cm long and 2–5 mm broad, with a pointed leaf tip.
The stem system of the plant will grow until it reaches the surface of the water, where it will begin to spread out, creating a thick flower canopy that blocks light from reaching plants below it.
Brazilian waterweed, or Egeria densa, Perennial, floating or rooted. Elongate stems bear leaves in densely spaced whorls of 4-5 (particularly dense near apex). Leaves scale-like, sessile, linear, slightly recurved, with single mid-vein; margin finely serrate. Inflorescence axillary, of unisexual flowers. Female and male flowers similar in shape, opening above water surface; sepals 3; petals 3, white. Dispersal by seed and stem fragments.
Adventitious roots (unbranched) and lateral branches grow only from double nodes (specialized nodes separated by a shortened internode) typically spaced along stems at 6-12 node intervals. Only fragments containing a double node develop into new plants.
Egeria densa is often confused with other waterweeds such as; Elodea, Hydrilla, Lagarosiphon.
Brazilian waterweed can grow as a floating plant or anchored in the substrate. It can grow under almost any conditions, growing vigorously when in colder temperatures and hard water rich in calcium, however, it tolerates higher temperatures for a short time without slowing growth. Growth is slower in soft water areas. Brazilian waterweed does not require CO2 fertilisation, however, the presence of CO2 will speed up growth.
How To Identify Brazilian waterweed?
Brazilian waterweed - Egeria densa ID Guide
Leaf: Very fine toothed whorled green leaf 4-8 and 1-4 cm long with pointed tip
Flower: white with 3 petals and yellow stamen appear along stems, can grow up to 4m deep

Leaves

Flower
Why Is Brazilian waterweed A Problem?
Out competes native species. Most of its impact occurs in the shallow waterways; the plant forms thick mats that obstruct boat passage, clog water intakes and aqueducts, trap sediments, crowd out native vegetation, and impede the migration of anadromous fish.
European Communities (Birds and Natural Habitats) Regulations 2011 non-native invasive plant species A-Z (Updated 2017)
There are currently 35 invasive plant species listed in the European Communities (Birds and Natural Habitats) Regulations (annex 2, Part 1)...
Click on a species from the following list to find out more regarding non-native species subject to restrictions under Regulations 49 and 50.
-
American Skunk-Cabbage - Lysichiton americanus
-
Brazilian Giant-Rhubarb - Gunnera manicata
-
Broad-Leaved Rush - Juncus planifolius
-
Cape Pondweed - Aponogeton distachyos
-
Cord-Grasses - Spartina (all species and hybrids)
-
Curly Waterweed - Lagarosiphon major
-
Dwarf Eel-Grass - Zostera japonica
-
Fanwort - Cabomba caroliniana
-
Floating Pennywort - Hydrocotyle ranunculoides
-
Fringed Water-Lily - Nymphoides peltata
-
Giant Hogweed - Heracleum mantegazzianum
-
Giant Knotweed - Fallopia sachalinensis
-
Giant-Rhubarb - Gunnera tinctoria
-
Giant Salvinia - Salvinia molesta
-
Himalayan Balsam - Impatiens glandulifera
-
Himalayan Knotweed - Persicaria wallichii
-
Hottentot-Fig - Carpobrotus edulis
-
Japanese Knotweed - Fallopia japonica
-
Large-Flowered Waterweed - Egeria densa
-
Mile-a-Minute Weed - Persicaria perfoliata
-
New Zealand Pigmyweed - Crassula helmsii
-
Parrots Feather - Myriophyllum aquaticum
-
Red Alga - Grateloupia doryphora
-
Rhododendron - Rhododendron ponticum
-
Salmonberry - Rubus spectabilis
-
Sea-Buckthorn - Hippophae rhamnoides
-
Spanish Bluebell - Hyacinthoides hispanica
-
Three-Cornered Leek - Allium triquetrum
-
Wakame - Undaria pinnatifida
-
Water Chestnut - Trapa natans
-
Water Fern - Azolla filiculoides
-
Water Lettuce - Pistia stratiotes
-
Water-Primrose - Ludwigia (all species)
-
Waterweeds - Elodea (all species)
-
Wireweed - Sargassum muticum
Non-Native Plant Species identified as High Risk on Ireland's Biodiversity List...
Common name
Species name
Environment
Terrestrial
Freshwater
Terrestrial
Terrestrial
Marine
Freshwater
Freshwater
Freshwater
Terrestrial
Terrestrial
Terrestrial
Terrestrial
Marine
Terrestrial
Freshwater
Freshwater
Freshwater
Terrestrial
Freshwater
Marine
Risk score
20
19
18
19
18
19
21
20
19
18
18
19
19
20
20
19
20
20
20
18
Additional Non-Native Plant Species identified as Medium Risk on Ireland's Biodiversity List...
Common name
Barberry
Brazilian waterweed
Butterfly-bush
Canadian-fleabane
Clover broomrape
False acacia
Garden lupin
Giant rhubarb
Hairy rocket
Himalayan honeysuckle
Himalayan knotweed
Holm oak
Pampas grass
Pitcherplant
Red oak
Rock cotoneaster
Salmonberry
Sycamore
Three-cornered garlic
Traveler's-joy
Species name
Lysichiton americanus
Antithamnionella ternifolia
Ribes nigrum
Egeria densa
Buddleja davidii
Conyza canadensis
Codium fragile ssp. tomentosoides
Pseudotsuga menziesii
Solidago gigantea
Gunnera manicata
Persicaria wallichii
Lonicera japonica
Euphorbia esula
Acaena ovalifolia
Matteuccia struthiopteris
Sarracenia purpurea
Bunias orientalis
Environment
Terrestrial
Terrestrial
Terrestrial
Marine
Terrestrial
Terrestrial
Freshwater
Terrestrial
Terrestrial
Terrestrial
Terrestrial
Marine
Terrestrial
Terrestrial
Terrestrial
Terrestrial
Terrestrial
Terrestrial
Terrestrial
Terrestrial
Terrestrial
Terrestrial
Terrestrial
Terrestrial
Terrestrial
Terrestrial
Freshwater
Terrestrial
Terrestrial
Terrestrial
Terrestrial
Terrestrial
Terrestrial
Marine
Terrestrial
Terrestrial
Terrestrial
Terrestrial
Terrestrial
Terrestrial
Terrestrial
Terrestrial
Terrestrial
Terrestrial
Terrestrial
Terrestrial
Freshwater
Terrestrial
Risk score
14
15
17
15
14
14
17
17
14
17
16
16
15
14
17
17
17
16
17
14
16
14
14
15
14
16
14
16
14
14
14
14
14
14
14
17
14
14
14
15
15
17
17
14
16
15
14
15